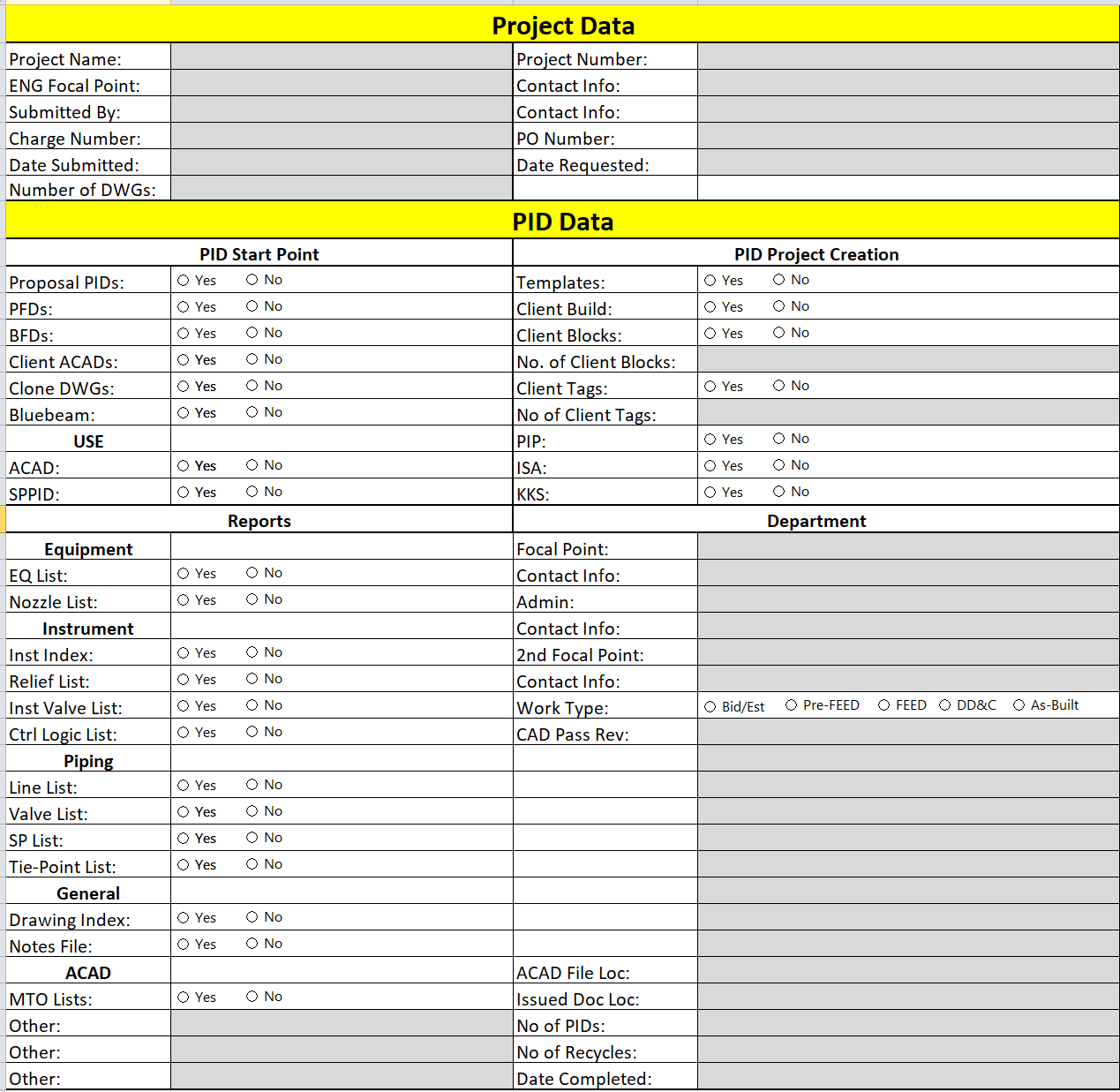
Technical Information
What is Metadata? -
Metadata is data that describes other data. Meta is a prefix that in most information technology usages means "an underlying definition or description." Metadata summarizes basic information about data, which can make finding and working with particular instances of data easier.
What are some basic Metadata types?
Server - This is the house of the whole system
Architecture - This is the pathing and connecting of the Smart Tools and content in the Server
Document Management (DMS) - This system is how to find and read documents using search engines and DMS tools
Document File Level - Document File Metadata (Properties/Title/Etc.) Can also be the content in the Title Blocks for Drawings
PAU - Plant/Area/Unit - This is the waterfall 3 tier system for organizing object data in a project
Plant/Project ID/Site - Client Name/WBS Number/Client Site ID/Global Asset ID
Area - Plants in a site/Process Units/CWA Zones
Unit - Sub-System/System/Department/District
Drawing/Document Content Level
Title Data/Border Data - What?
Revision Data - Who when why?
Objects
Object Family - Grouping of like content with a set rule set for identification and behavior (Equipment)
Class - Like objects in a select classification (Vessel)
Sub-Class - The set above sorted down even smaller (Horizontal Vessel)
Type - The actual object (KO Drum)
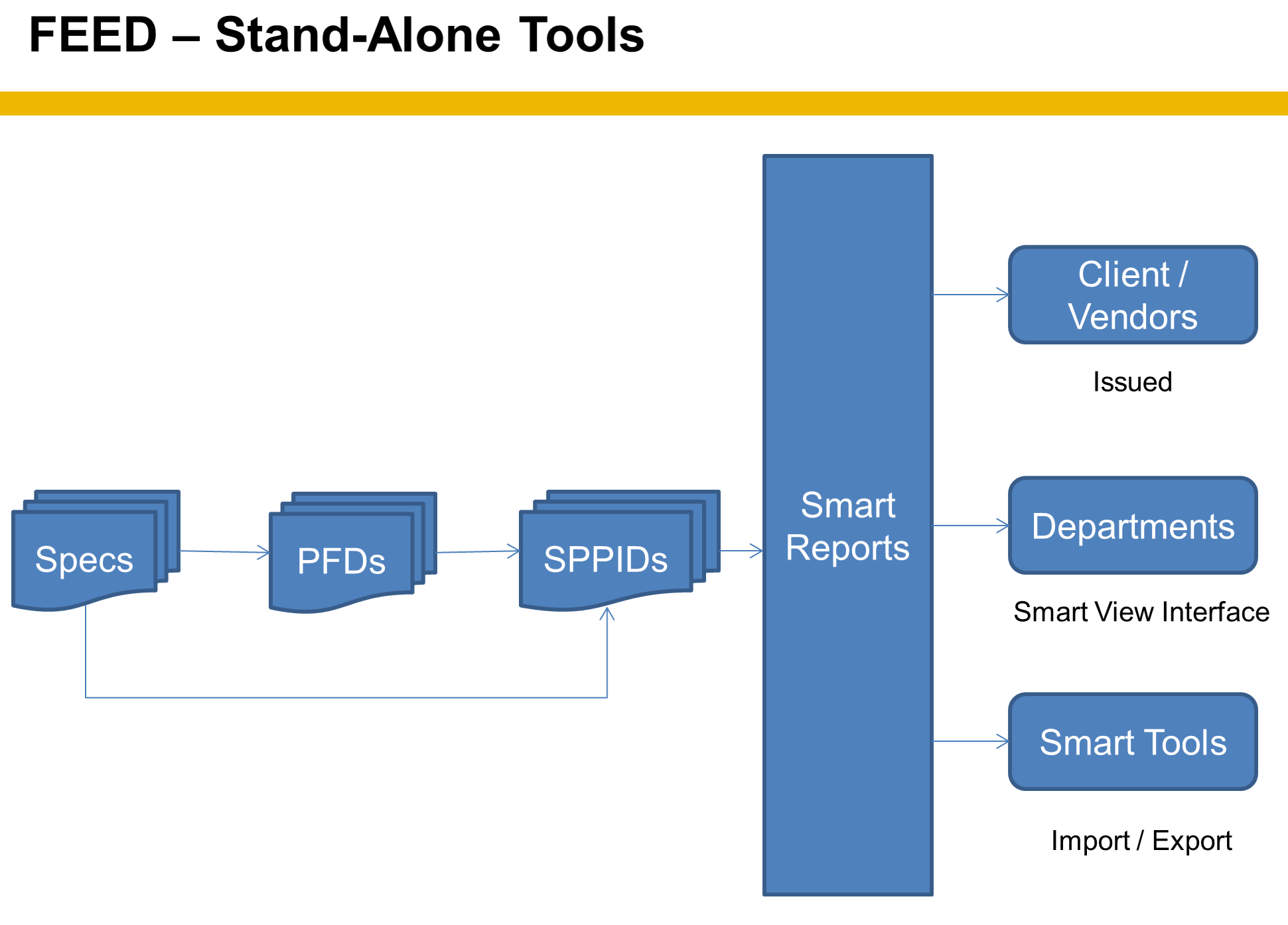
Pre-FEED/FEED Stand Alone System
A Pre-FEED Stand Alone system - This where your Smart tools are used as individual tools with limited data sharing if any. (Not Integrated)
Pro
Lower costs and skill level of users required
Works more like traditional CAD/ACAD workflows (Picture Driven)
Short Form PIDs and PFD/PID Hybrid options are possible in this format
Object Reporting is possible
Con
Reports are export only, 3rd party tools needed to share data
End product is not normally at a good enough Level of Detail (LOD) for end users
Content has to be redrawn if not in Long Form formatting
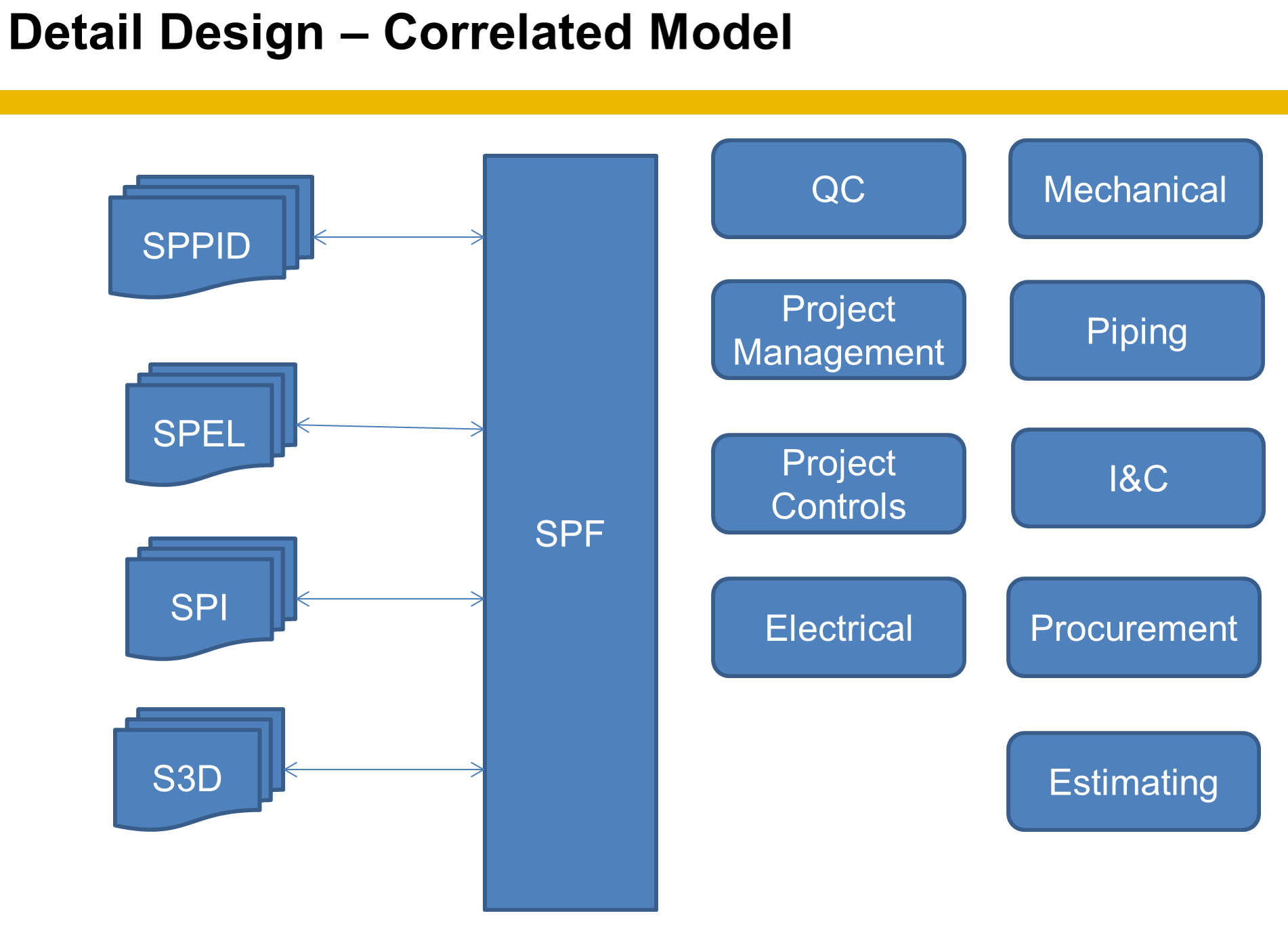
Detailed Design/Construction/Operations Integrated System
A Detail Design Integrated system - This where your Smart tools are used together to validate content and share metadata results.
Pro
Engineering costs shift to CAD Services and IT
Content errors can be avoided with Digital Twin error checking, Auditing Services, and Data integrity tools
Content can become rule based/automated (Automation is where internal software AI does the validation)
Client formatting can be enforced
Con
High costs and high skill level of users required
Can take up to five years to fully develop
Can cause the company workflows as they know them to all change